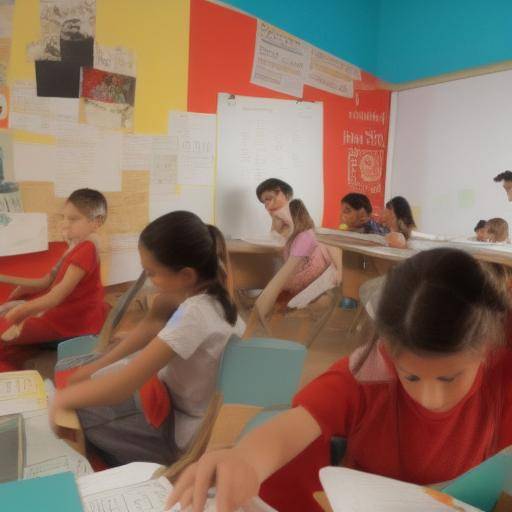
Introduction
The structured game, also known as directed game or guided game, plays a crucial role in the cognitive, emotional and social development of children in their early years of life. In this article, we will thoroughly explore the importance of the structured game in early education, its historical evolution, detailed analysis, practical advice and future perspectives. In addition, we will examine the relationship between formal play, education and early age to provide a holistic view on this fundamental issue in child development.
History and Background
The concept of structured play has its roots in the theories of child development of renowned psychologists and educators such as Jean Piaget and Lev Vygotsky. Throughout history, the focus on guided play has evolved significantly, from simply being a form of entertainment to being recognized as a fundamental tool for the learning and socialization of children at an early age. From the old forms of guided play in different cultures to the creation of specific teaching methods and programs, the structured game has experienced continuous development that has shaped contemporary educational practices.
The structured game has been the subject of major studies and research that have demonstrated their benefits in child development. Significant advances in neuroscience and psychology have supported the importance of this approach, providing a solid scientific basis for its implementation in educational settings. In addition, the collaboration of pedagogues, occupational therapists and other professionals has broadened the horizons of the structured game, achieving a diverse and effective integration into various educational and therapeutic frameworks.
Analysis in Deep
The structured game offers a wide range of benefits for the development of children, including improving cognitive, social, emotional and motor skills. Studies have shown that the structured game encourages problem solving, critical thinking, cooperation and self-expression. It also gives children the opportunity to explore their environment, strengthen their linguistic skills and develop a solid understanding of abstract concepts.
Despite its many advantages, the structured game also poses challenges, such as the need to balance the child's creative freedom with the pedagogical direction. Educators and parents must be aware of the specific limitations and considerations in implementing the structured game, ensuring that they provide a safe and enriching environment that promotes the integral development of the child.
Comprehensive review
The effective implementation of the structured game in educational settings requires a detailed understanding of the methodologies, resources and strategies involved. Furthermore, the adaptation of the structured game to the individual needs of each child and the recognition of cultural diversity are essential aspects that need to be addressed in the context of early education.
Comparative analysis
The intersection between structured play, education and early age reveals a holistic integration that enriches child development. The complementarity between structured play and formal educational approaches at early stages of a child ' s life is critical to providing a solid foundation that encourages continuous learning and personal growth.
Practical Tips and Advice
In considering the implementation of the structured game in educational and child-care settings, it is essential to adopt a balanced approach that promotes active participation and reflective learning. Educators and caregivers can effectively integrate structured play strategies by setting clear goals, providing individualized guidance and evaluating the progress of children in an inclusive manner.
Industry Perspectives and Expert Reviews
Experts in the field of early education, child psychology and cognitive development agree that the structured game is a fundamental component for the integral growth of children. With a focus on the development of crucial skills and the promotion of an active learning mentality, the structured game has become an indispensable pillar in early childhood education programmes.
Case Studies and Applications in Real Life
The positive impact of the structured game is reflected in many cases of study, where its influence is evident in the academic, emotional and social progress of children. These cases provide concrete examples of how the proper implementation of the structured game has contributed significantly to the development of adaptive skills, autonomy and problem solving in children from different social and cultural contexts.
Future Trends and Predictions
As prospects for early education continue to evolve, the structured game is expected to continue to play a crucial role in the global educational landscape. Pedagogical practices are expected to be further enriched by integrating innovative approaches and emerging technologies that enhance the effectiveness of the structured game as a learning and development tool.
Conclusion
The structured game in early education represents an essential component for the holistic development of children, providing an enriching environment that fosters learning, creativity, resilience and self-confidence. Recognizing its positive impact and capacity to enhance child growth, it is essential to prioritize its integration into educational programmes and childcare settings. The structured game emerges as well as a dynamic vehicle that promotes child development, preparing children for a promising future in the academic, social and emotional spheres.
Frequently asked questions
1. What is the difference between structured game and unstructured game?
The structured game is run by adults or educators, with specific learning objectives, while the unstructured game is more spontaneous and free, allowing children to explore without a direct guide.
2. What are the benefits of the structured game in early education?
The structured game promotes the development of cognitive, social, emotional and motor skills; stimulates creativity, fosters cooperation and contributes to the integral growth of children.
3. How old can the structured game begin in early education?
The structured game can be implemented in early ages, adapting to the individual capacities and needs of children. Early education programmes tend to integrate the structured game from the early years of life.
4. How can parents foster structured play at home?
Parents can promote the structured game by providing an enabling environment for learning, providing educational materials and actively participating in targeted activities that stimulate the growth and development of their children.
5. Is the structured game applicable to different cultural contexts?
Yes, the structured game can adapt to various cultural contexts, recognizing the differences and particularities of each community to ensure their effectiveness and inclusion.
6. What is the role of educators in the implementation of the structured game?
Educators play a key role in planning, guiding and evaluating the structured game, ensuring that educational goals are met and that the individual progress of each child is adequately addressed.
Concluding, the structured game in early education is a cornerstone that moulds the holistic development of children, offering a solid and enriching approach that enhances their growth and learning in the early stages of life. Its impact will extend through cognitive, social, emotional and motor benefits, preparing children for a promising future while cultivating a lasting appreciation for learning and exploration. It is essential to recognize and promote the integration of structured play into educational and child-care environments, encouraging comprehensive development that encourages children to a path of discovery and achievements in their educational journey.